Congratulations to George, Dina and our collaborators at OCT Medical and UCSD on developing the first biomolecular, genetically encodable contrast agents for for optical coherence tomography based on the optical properties of gas vesicles.

Lu GJ, Chou L, Malounda D, Patel AK, Welsbie DS, Chou DL*, Ramalingam T*, Shapiro MG*. Biomolecular contrast agents for optical coherence tomography Submitted. bioRxiv preprint




 Congratulations to Pradeep, Sonjong, Hunter, Audrey, Vivek, Max, Jenny and Vasant on their new work showing that strong cellular paramagnetism is sufficient for magnetic manipulation and MRI contrast. Their genetic circuit makes bacteria “ultraparamagnetic” by oxidizing and chelating iron in a ferrogel.
Congratulations to Pradeep, Sonjong, Hunter, Audrey, Vivek, Max, Jenny and Vasant on their new work showing that strong cellular paramagnetism is sufficient for magnetic manipulation and MRI contrast. Their genetic circuit makes bacteria “ultraparamagnetic” by oxidizing and chelating iron in a ferrogel. Congratulations to
Congratulations to 


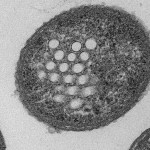
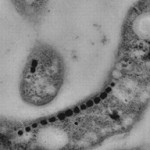
 Congratulations to Ray, Audrey, Anu, Arash, Priya and Suchita on their work on acoustic reporter genes, featured on the cover of Nature!
Congratulations to Ray, Audrey, Anu, Arash, Priya and Suchita on their work on acoustic reporter genes, featured on the cover of Nature!