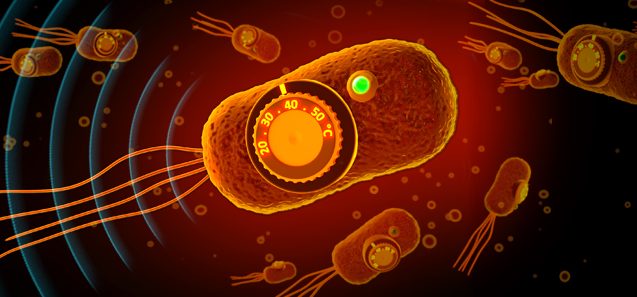
 Congratulations to Anu, Zhiyang, Suchita and colleagues on their new paper in Nature Chemical Biology describing the first acoustic biosensors. These biosensors turn on nonlinear ultrasound contrast in response to protease activity. This allows the action of enzymes such as TEV, Calpain and ClpXP to be visualized in cells deep inside the body.
Congratulations to Anu, Zhiyang, Suchita and colleagues on their new paper in Nature Chemical Biology describing the first acoustic biosensors. These biosensors turn on nonlinear ultrasound contrast in response to protease activity. This allows the action of enzymes such as TEV, Calpain and ClpXP to be visualized in cells deep inside the body.
Lakshmanan A#, Jin Z#, Nety SP, Sawyer DP, Lee-Gosselin A, Malounda D, Swift MB, Maresca D, Shapiro MG*. Acoustic biosensors for ultrasound imaging of enzyme activity. Nature Chemical Biology 16, 988-986 (2020).
article | readcube | behind the paper | press
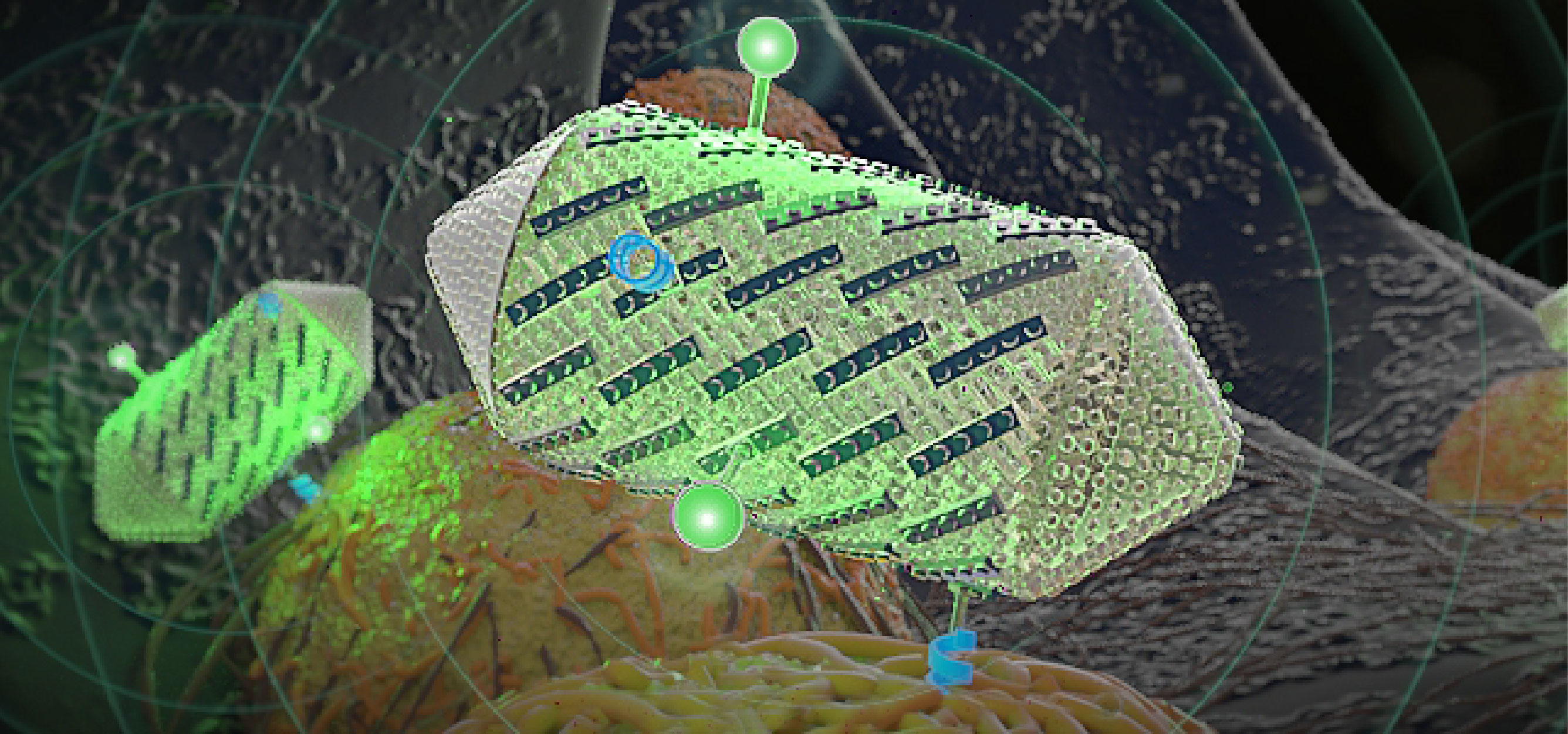
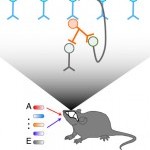



 Congratulations to Dan and Echo on their publication describing modular protein domains with sharp, tunable, temperature-dependent heterodimerization. Fusing these domains with other proteins provides control over their association and localization using temperature, which can be delivered globally and locally using methods such as focused ultrasound and magnetic hyperthermia.
Congratulations to Dan and Echo on their publication describing modular protein domains with sharp, tunable, temperature-dependent heterodimerization. Fusing these domains with other proteins provides control over their association and localization using temperature, which can be delivered globally and locally using methods such as focused ultrasound and magnetic hyperthermia.
 Congratulations to David, Audrey, Bill, Dina and collaborators in Paris on demonstrating enhanced non-invasive imaging of neural activity in mice using intravascular gas vesicles as boosters of hemodynamic functional ultrasound contrast.
Congratulations to David, Audrey, Bill, Dina and collaborators in Paris on demonstrating enhanced non-invasive imaging of neural activity in mice using intravascular gas vesicles as boosters of hemodynamic functional ultrasound contrast. Congratulations to
Congratulations to 
